项目稳定运行快一年,没有过关于发http请求的问题,但是最近由于第三方频繁”变动”,项目集中爆发apache httpclient相关的一些“事故”,所以事后整理做个记录:
1 关于keepalive和DNS cache
问题描述: 产线某个组件使用了DNS切换的方式来做Failover, 基本流程Primary->Backup,然后从Backup->Primary(区别在于Failback回来时,并无关闭或者重启Backup),
当Failback回来时,一个feature就不work了。
问题跟踪: 拿到这个问题时,首先定位到原因: Failback时,连接仍然连接在Backup。而刚好由于第三方某个bug,当一个业务的所有请求不完全落在一个DC时,就会不work, 虽然说fix这个问题,功能就可以正常,但是不符合优先选择primary的策略(假设确实有权重的话)。
拿到这个问题后,第一怀疑是DNS Cache问题,因为failover是使用DNS的方式,所以第一怀疑到这个上面:
(1)排除主机DNS Cache: 直接使用ping或者traceroute:
[root@jiafu conf]# traceroute www.baidu.com traceroute to www.baidu.com (104.193.88.123), 30 hops max, 60 byte packets 1 10.224.2.1 (10.224.2.1) 0.502 ms 0.783 ms 0.782 ms 2 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1) 0.899 ms 1.042 ms 1.116 ms
(2) 排除应用层Cache: 我们知道JVM内部也是有dns cache的。
但是使用下面程序“嵌入”到服务器代码中测试了下,并无任何缓存:
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class DNSCache {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InetAddress.getByName("www.google.com");
try {
InetAddress.getByName("nowhere.example.com");
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
}
String addressCache = "addressCache";
System.out.println(addressCache);
printDNSCache(addressCache);
String negativeCache = "negativeCache";
System.out.println(negativeCache);
printDNSCache(negativeCache);
}
private static void printDNSCache(String cacheName) throws Exception {
Class<InetAddress> klass = InetAddress.class;
Field acf = klass.getDeclaredField(cacheName);
acf.setAccessible(true);
Object addressCache = acf.get(null);
Class cacheKlass = addressCache.getClass();
Field cf = cacheKlass.getDeclaredField("cache");
cf.setAccessible(true);
Map<String, Object> cache = (Map<String, Object>) cf.get(addressCache);
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> hi : cache.entrySet()) {
Object cacheEntry = hi.getValue();
Class cacheEntryKlass = cacheEntry.getClass();
Field expf = cacheEntryKlass.getDeclaredField("expiration");
expf.setAccessible(true);
long expires = (Long) expf.get(cacheEntry);
Field af = cacheEntryKlass.getDeclaredField("address");
af.setAccessible(true);
InetAddress[] addresses = (InetAddress[]) af.get(cacheEntry);
List<String> ads = new ArrayList<String>(addresses.length);
for (InetAddress address : addresses) {
ads.add(address.getHostAddress());
}
System.out.println(hi.getKey() + " "+new Date(expires) +" " +ads);
}
}
}
排查后,并无任何缓存记录。继续跟踪了下:原来项目中在启动参数使用-Dsun.net.inetaddr.ttl=0里面关闭了JVM的DNS cache:
sun.net.InetAddressCachePolicy
// Controls the cache policy for successful lookups only
private static final String cachePolicyProp = "networkaddress.cache.ttl";
private static final String cachePolicyPropFallback =
"sun.net.inetaddr.ttl";
public static final int FOREVER = -1;
public static final int NEVER = 0;
/* default value for positive lookups */
public static final int DEFAULT_POSITIVE = 30; //默认30s
Integer tmp = java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<Integer>() {
public Integer run() {
try {
String tmpString = Security.getProperty(cachePolicyProp); //判断有没有设置networkaddress.cache.ttl
if (tmpString != null) {
return Integer.valueOf(tmpString);
}
} catch (NumberFormatException ignored) {
// Ignore
}
try {
String tmpString = System.getProperty(cachePolicyPropFallback); //判断有没有设置sun.net.inetaddr.ttl
if (tmpString != null) {
return Integer.decode(tmpString);
}
} catch (NumberFormatException ignored) {
// Ignore
}
return null;
}
});
if (tmp != null) {
cachePolicy = tmp.intValue();
if (cachePolicy < 0) {
cachePolicy = FOREVER; //永久cache
}
propertySet = true;
} else {
/* No properties defined for positive caching. If there is no
* security manager then use the default positive cache value.
*/
if (System.getSecurityManager() == null) {
cachePolicy = DEFAULT_POSITIVE; //设置成默认30s
}
}
每次DNS解析后,都调用上面代码设置的policy存cache,例如30s或者不存等等:
java.net.InetAddress
/**
* Add an entry to the cache. If there's already an
* entry then for this host then the entry will be
* replaced.
*/
public Cache put(String host, InetAddress[] addresses) {
int policy = getPolicy();
if (policy == InetAddressCachePolicy.NEVER) {
return this;
}
// purge any expired entries
if (policy != InetAddressCachePolicy.FOREVER) {
// As we iterate in insertion order we can
// terminate when a non-expired entry is found.
LinkedList<String> expired = new LinkedList<>();
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (String key : cache.keySet()) {
CacheEntry entry = cache.get(key);
if (entry.expiration >= 0 && entry.expiration < now) {
expired.add(key);
} else {
break;
}
}
for (String key : expired) {
cache.remove(key);
}
}
// create new entry and add it to the cache
// -- as a HashMap replaces existing entries we
// don't need to explicitly check if there is
// already an entry for this host.
long expiration;
if (policy == InetAddressCachePolicy.FOREVER) {
expiration = -1;
} else {
expiration = System.currentTimeMillis() + (policy * 1000);
}
CacheEntry entry = new CacheEntry(addresses, expiration);
cache.put(host, entry);
return this;
}
(3)锁定长连接问题:
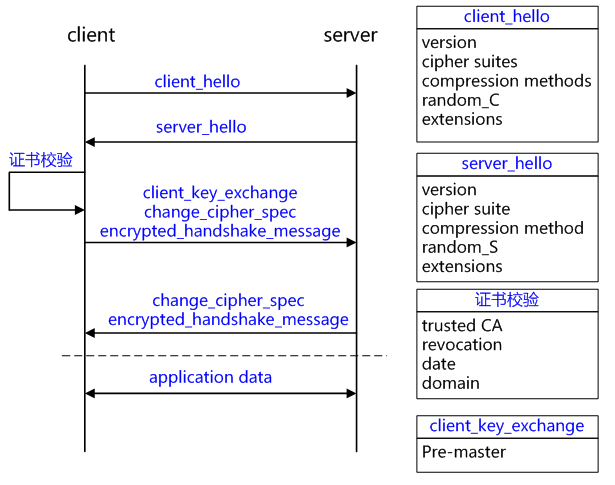
查看协议,在http1.1协议中,默认就是长连接,除非显式加上header: Connection: close. 所以apache http client在拿到一个响应时,默认是按照长连接来处理的,所以除非打断连接(例如重启机器或者LB).否则无法重新做连接。
基本逻辑:涉及2个策略:reuseStrategy控制是否重用,keepAliveStrategy控制重用多久。
整体逻辑实现:org.apache.http.impl.execchain.MainClientExec:
// The connection is in or can be brought to a re-usable state.
if (reuseStrategy.keepAlive(response, context)) {
// Set the idle duration of this connection
final long duration = keepAliveStrategy.getKeepAliveDuration(response, context);
if (this.log.isDebugEnabled()) {
final String s;
if (duration > 0) {
s = "for " + duration + " " + TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS;
} else {
s = "indefinitely";
}
this.log.debug("Connection can be kept alive " + s);
}
connHolder.setValidFor(duration, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
connHolder.markReusable();
} else {
connHolder.markNonReusable();
}
org.apache.http.impl.DefaultConnectionReuseStrategy 策略决定是否keepalive
HeaderIterator hit = response.headerIterator(HTTP.CONN_DIRECTIVE);
if (hit.hasNext()) {
try {
TokenIterator ti = createTokenIterator(hit);
boolean keepalive = false;
while (ti.hasNext()) {
final String token = ti.nextToken();
if (HTTP.CONN_CLOSE.equalsIgnoreCase(token)) { //对端显示返回Connection:close
return false;
} else if (HTTP.CONN_KEEP_ALIVE.equalsIgnoreCase(token)) {
// continue the loop, there may be a "close" afterwards
keepalive = true;
}
}
if (keepalive)
return true;
// neither "close" nor "keep-alive", use default policy
} catch (ParseException px) {
// invalid connection header means no persistent connection
// we don't have logging in HttpCore, so the exception is lost
return false;
}
}
org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultConnectionKeepAliveStrategy 策略决定keepalive多久
public class DefaultConnectionKeepAliveStrategy implements ConnectionKeepAliveStrategy {
public long getKeepAliveDuration(HttpResponse response, HttpContext context) {
if (response == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("HTTP response may not be null");
}
HeaderElementIterator it = new BasicHeaderElementIterator(
response.headerIterator(HTTP.CONN_KEEP_ALIVE));
while (it.hasNext()) {
HeaderElement he = it.nextElement();
String param = he.getName();
String value = he.getValue();
if (value != null && param.equalsIgnoreCase("timeout")) { //http协议草案,大多实现,但是不是强制要求
try {
return Long.parseLong(value) * 1000;
} catch(NumberFormatException ignore) {
}
}
}
return -1; //永久连接。
}
}
org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultClientConnectionReuseStrategy另外一个子策略的继承类,加了“请求端connection header的判断”:
@Override
public boolean keepAlive(final HttpResponse response, final HttpContext context) {
final HttpRequest request = (HttpRequest) context.getAttribute(HttpCoreContext.HTTP_REQUEST);
if (request != null) {
final Header[] connHeaders = request.getHeaders(HttpHeaders.CONNECTION); //处理request的
if (connHeaders.length != 0) {
final TokenIterator ti = new BasicTokenIterator(new BasicHeaderIterator(connHeaders, null));
while (ti.hasNext()) {
final String token = ti.nextToken();
if (HTTP.CONN_CLOSE.equalsIgnoreCase(token)) {
return false;
}
}
}
}
return super.keepAlive(response, context); //调用上层策略,即response的header的处理
}
解决方案:
(1)在服务器端的响应中,添加header: Connection:close,本地测试通过,但是上线通过VIP后失效,VIP直接将这个头扔掉
(2)在客户端的请求中,添加header:Connection: close,本地和上线都能通过,这种实际上把长连接主动变成了短连接,失去了长连接的优势
(3)仅仅将长连接的“时长”控制在一个时间范围内,比如3分钟。这样每到3分钟后,就自动重新连接,既一定程度保留了长连接的优势,也兼顾了可以做“切换”DNS的可能性。
但是每个人都会问同一个问题:设置几分钟合理?所以最好是由server来告知,但是这个在http协议中并无规定如何实现,所以http draft中层提及keepalive: timeout,这种确实在apache http client中支持,但是在当前比较流行的ok http client并不支持。
所以综合起来看,方案3是最合理的方案,同时在服务器应用设计时,应该让所有客户端提前知道这件事情,不然很容易“犯错”而产生质疑:“你没有遵循或者协商过要求我主动断连接,我遵循协议还有错?”
2 关于SNI支持
屋漏更糟连夜雨,还没来得及改完,另外的问题又来了。
问题描述: 某第三方从rackspace迁移至aws.在迁移后,应用直接报证书不批配错误:
Caused by: javax.net.ssl.SSLException: hostname in certificate didn't match: <xxxx.com> != <.yyy.com> at org.apache.http.conn.ssl.AbstractVerifier.verify(AbstractVerifier.java:227) at org.apache.http.conn.ssl.BrowserCompatHostnameVerifier.verify(BrowserCompatHostnameVerifier.java:54) at org.apache.http.conn.ssl.AbstractVerifier.verify(AbstractVerifier.java:147) at org.apache.http.conn.ssl.AbstractVerifier.verify(AbstractVerifier.java:128) at org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLSocketFactory.connectSocket(SSLSocketFactory.java:439) at org.apache.http.impl.conn.DefaultClientConnectionOperator.openConnection(DefaultClientConnectionOperator.java:180) at org.apache.http.impl.conn.ManagedClientConnectionImpl.open(ManagedClientConnectionImpl.java:294) at org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultRequestDirector.tryConnect(DefaultRequestDirector.java:643) at org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultRequestDirector.execute(DefaultRequestDirector.java:479) at org.apache.http.impl.client.AbstractHttpClient.execute(AbstractHttpClient.java:906) at org.apache.http.impl.client.AbstractHttpClient.execute(AbstractHttpClient.java:805) at org.jboss.resteasy.client.jaxrs.engines.ApacheHttpClient4Engine.invoke(ApacheHttpClient4Engine.java:283
问题跟踪:
本来怀疑比较多,想下我方应用并无改动,肯定不是我方问题,估计是对方证书什么搞错了,后来也翻看了下源码,验证了下想法:
1 final Certificate[] certs = session.getPeerCertificates(); 2 final String cn = DefaultHostnameVerifier.extractCN(subjectPrincipal.getName(X500Principal.RFC2253)); 3 void verify(String host, String[] cns, String[] subjectAlts)
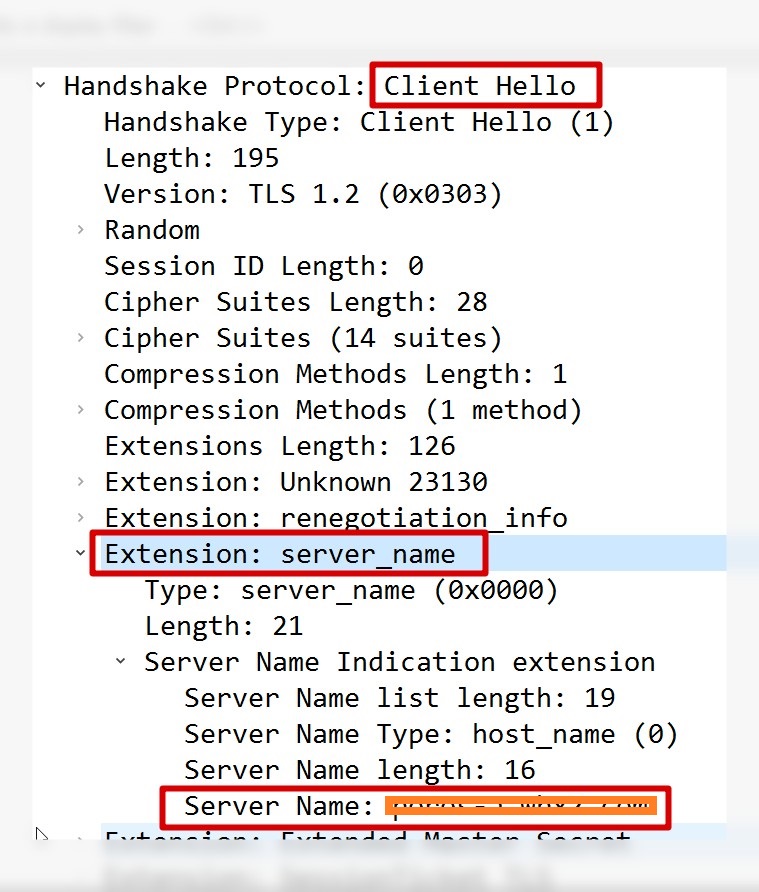
基本就是访问那个主机,拿到证书,和自己访问的url可匹配。后来仔细了解了背景,这个服务部署做了迁移,做了SNI的支持,即支持不同域名来访问,然后客户端在拿证书时,需要带上自己访问的域名,以返回正确的证书,而不带的话,返回默认的。
使用openssl演示下:
openssl s_client -connect 130.59.223.53:443 CONNECTED(00000003) depth=3 C = US, O = "The Go Daddy Group, Inc.", OU = Go Daddy Class 2 Certification Authority verify return:1 depth=0 OU = Domain Control Validated, CN = *.yy.com verify return:1
带上主机名后:
openssl s_client -connect 130.59.223.53:443 -servername xx.com CONNECTED(00000003) depth=3 C = US, O = "The Go Daddy Group, Inc.", OU = Go Daddy Class 2 Certification Authority verify return:1 depth=0 OU = Domain Control Validated, CN = *.xx.com //返回了正确的证书 verify return:1
问题解决:
了解基本情况后,google了httpclient的SNI支持,在4.3.2+才支持,而自己用的版本略低(4.2.6),查看4.3.2的release时间是2014年,刚好是项目启动之时,悲剧。
所以直接升级httpclient,但是测试发现仍然不work,原来,虽然升级了,但是原有代码的使用方式是不支持sni的deprecated的code方式。这种情况特别容易发生在间接调用的情况下(例如我这里的案例,外面套了一层jboss的rest client,调用了httpclient的deprecated code)。
https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/HTTPCLIENT-1119
sun.security.ssl.Handshaker
/**
* Sets the server name indication of the handshake.
*/
void setSNIServerNames(List<SNIServerName> serverNames) {
// The serverNames parameter is unmodifiable.
this.serverNames = serverNames;
}
sun.security.ssl.ClientHandshaker
// add server_name extension
if (enableSNIExtension) {
if (session != null) {
requestedServerNames = session.getRequestedServerNames();
} else {
requestedServerNames = serverNames;
}
if (!requestedServerNames.isEmpty()) {
clientHelloMessage.addSNIExtension(requestedServerNames);
}
}
tcpdump可以知道,支持SNI的请求第一步”client hello”会带上servername:
3 关于连接失效检测
当完成第二步升级之后,基本对httpclient的源码有个大体了解,想起之前在升级前和另外一个第三方做集成时,每次都做stable check失败。所以继续翻阅了httpclient的代码。发现一个升级后潜在的问题,最后测试验证确实如此。
(1)为什么要做连接检测:
httpclient使用的是传统的io模式,所以一旦长连接建立并且使用完后,归回connection manager,这个时候,它既不处于读也不处于写操作状态,因为也没有必要,因为http的是请求-》响应模式,根据content-length或者chunk方式读完后,没有必要继续等待数据。所以这个时候归还connection manager给接下的请求使用。但是就是因为它闲置了,所以没有办法检测到对端连接关闭,下次使用时直接会报错。
而对于nio,引用一段话:
The only time you need a selector to detect a closed channel is the case where the peer closes it, in which case select() will trigger with OP_READ/isReadable(), and a subsequent read() will return -1.
所以无论使用IO还是NIO,只要不读的时候,即使底层有通知,也需要上层来处理。
(2)怎么做连接检测:
连接检测主要就是担心连接失效。所以可以预防着做:例如连接使用5分钟就自动不用了(expire),或者另外一种方式,闲置了5分钟就直接不要了(idle),而不需要做什么检测。
setConnectionTimeToLive(3, TimeUnit.MINUTES). evictExpiredConnections(). evictIdleConnections(1, TimeUnit.MINUTES).
但是使用这种方式都是预防性的方式,还有主动性的方式:例如升级前的httpclient在每个请求复用旧连接时,都会检查一次是否失效了。但是这样效率比较低,因为事先如果就已经约定好是长连接的话,何必又处处设防于每次请求都浪费时间做check,明显并不高效。所以新版本的httpclient做了改善,deprecate了老版本的每个请求检查,使用了一个validateAfterInactivity参数来控制,一个连接使用时,发现已经过了某个时间期就来检测一次。从而减少检查次数。
了解基本原理后,考虑一个情况:假设一个第三方不遵循http1.1的协议,告诉你是个长连接,但是响应你的请求后,立马又断连,可能会出现什么情况:
拿到一个连接后,还没有到检查时候,也不符合idle和expire条件时,这个时候,直接就fail了。除非把默认关闭的“废弃的”stable check打开。
Caused by: org.apache.http.NoHttpResponseException: The target server failed to respond at org.apache.http.impl.conn.DefaultHttpResponseParser.parseHead(DefaultHttpResponseParser.java:143) at org.apache.http.impl.conn.DefaultHttpResponseParser.parseHead(DefaultHttpResponseParser.java:57) at org.apache.http.impl.io.AbstractMessageParser.parse(AbstractMessageParser.java:261) at org.apache.http.impl.DefaultBHttpClientConnection.receiveResponseHeader(DefaultBHttpClientConnection.java:165) at org.apache.http.impl.conn.CPoolProxy.receiveResponseHeader(CPoolProxy.java:167) at org.apache.http.protocol.HttpRequestExecutor.doReceiveResponse(HttpRequestExecutor.java:272) at org.apache.http.protocol.HttpRequestExecutor.execute(HttpRequestExecutor.java:124) at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.MainClientExec.execute(MainClientExec.java:271) at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.ProtocolExec.execute(ProtocolExec.java:184) at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.RedirectExec.execute(RedirectExec.java:110) at org.apache.http.impl.client.InternalHttpClient.doExecute(InternalHttpClient.java:184) at org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient.execute(CloseableHttpClient.java:82) at org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient.execute(CloseableHttpClient.java:55) at org.jboss.resteasy.client.jaxrs.engines.ApacheHttpClient4Engine.invoke(ApacheHttpClient4Engine.java:312)
(3)如何做检查
org.apache.http.impl.BHttpConnectionBase
@Override
public boolean isStale() {
if (!isOpen()) {
return true;
}
try {
final int bytesRead = fillInputBuffer(1);
return bytesRead < 0; } catch (final SocketTimeoutException ex) { return false; } catch (final IOException ex) { return true; } } private int fillInputBuffer(final int timeout) throws IOException { final Socket socket = this.socketHolder.get(); final int oldtimeout = socket.getSoTimeout(); //取出原有设置的socket timeout时间 try { socket.setSoTimeout(timeout); //用上面设置的1ms来检查connection是否损坏,如果正常断开,立马返回-1.然后正常,会阻塞1ms. return this.inbuffer.fillBuffer(); } finally { socket.setSoTimeout(oldtimeout); //设置回去。 } } public int fillBuffer() throws IOException { // compact the buffer if necessary if (this.bufferpos > 0) {
final int len = this.bufferlen - this.bufferpos;
if (len > 0) {
System.arraycopy(this.buffer, this.bufferpos, this.buffer, 0, len);
}
this.bufferpos = 0;
this.bufferlen = len;
}
final int l;
final int off = this.bufferlen;
final int len = this.buffer.length - off;
l = streamRead(this.buffer, off, len);
if (l == -1) {
return -1;
} else {
this.bufferlen = off + l;
this.metrics.incrementBytesTransferred(l);
return l;
}
}
问题解决:
方案1: setStaleConnectionCheckEnabled(true),这个时候实际上等于把不推荐的方法开启了,和validateAfterInactivity这种控制有重复。
方案2: 要求对方遵循http规范: 处理完请求立马断连接应该加上header: Connection: close
方案3: 既然已经知道对方不遵循,对于这种应用,主动改成短连接。
setConnectionReuseStrategy(isKeepalive? DefaultConnectionReuseStrategy.INSTANCE: NoConnectionReuseStrategy.INSTANCE).
if(!isKeepalive) {
headers.put(HttpHeaderConstants.Keys.HEADER_CONNECTION, Arrays.asList("close"));
}
题外话:
(1)对于别人主动关闭自己的情况,自己会处于close wait状态(关闭需要双向关闭,主动关闭,会处于timewait),这个时候除非主动发现并关闭,否则一直处于这个状态,直至tcp层的keepalive,而tcp层默认是2小时。所以可以通过缩短这个时间来做一个保护:
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time=120
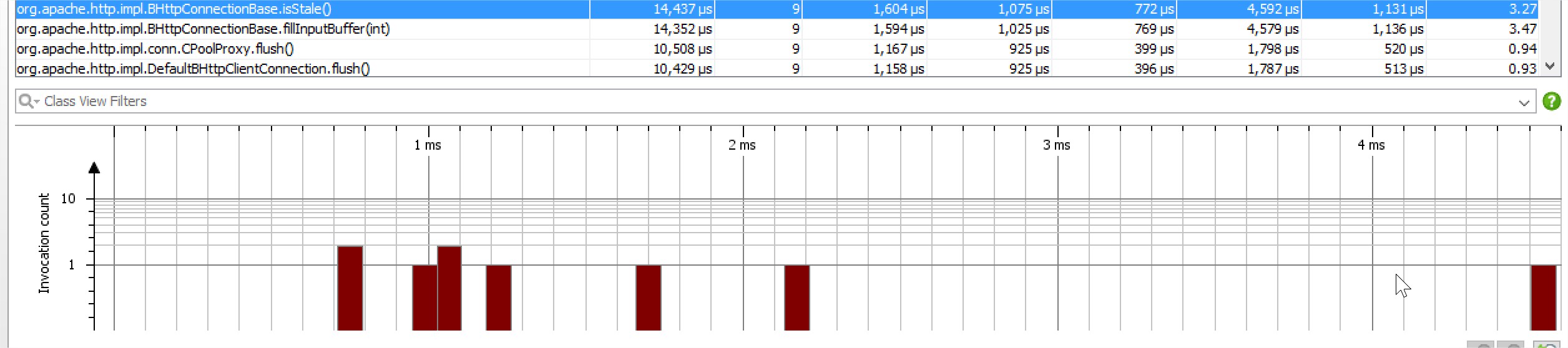
(2)文档说check isstable会浪费30ms时间,实际看源码不应该,因为也就阻塞等了1ms,所以用jprofiler测试了下,结果符合预期,基本都在2ms以内,不超过5ms:
问题: 偶然发现代码setConnectTimeout(2 * 1000)后,竟然有出现超时4s的情况:
现象:
Caused by: java.net.SocketTimeoutException: connect timed out //4s后才超时,而不是设置的2s
at java.net.PlainSocketImpl.socketConnect(Native Method)
at java.net.AbstractPlainSocketImpl.doConnect(AbstractPlainSocketImpl.java:350)
at java.net.AbstractPlainSocketImpl.connectToAddress(AbstractPlainSocketImpl.java:206)
at java.net.AbstractPlainSocketImpl.connect(AbstractPlainSocketImpl.java:188)
at java.net.SocksSocketImpl.connect(SocksSocketImpl.java:392)
at java.net.Socket.connect(Socket.java:589)
at org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLConnectionSocketFactory.connectSocket(SSLConnectionSocketFactory.java:337)
at org.apache.http.impl.conn.DefaultHttpClientConnectionOperator.connect(DefaultHttpClientConnectionOperator.java:141)
... 46 more
原因: DNS可能会解析出多笔记录,然后在连接时,挨个尝试。所以会出现超过设置的connection timeout情况。
org.apache.http.impl.conn.DefaultHttpClientConnectionOperator
@Override
public void connect(
final ManagedHttpClientConnection conn,
final HttpHost host,
final InetSocketAddress localAddress,
final int connectTimeout,
final SocketConfig socketConfig,
final HttpContext context) throws IOException {
final Lookup<ConnectionSocketFactory> registry = getSocketFactoryRegistry(context);
final ConnectionSocketFactory sf = registry.lookup(host.getSchemeName());
if (sf == null) {
throw new UnsupportedSchemeException(host.getSchemeName() +
" protocol is not supported");
}
final InetAddress[] addresses = host.getAddress() != null ?
new InetAddress[] { host.getAddress() } : this.dnsResolver.resolve(host.getHostName()); //解析出多个记录。
final int port = this.schemePortResolver.resolve(host);
for (int i = 0; i < addresses.length; i++) { final InetAddress address = addresses[i]; final boolean last = i == addresses.length - 1; //判断是不是最后一个 Socket sock = sf.createSocket(context); sock.setSoTimeout(socketConfig.getSoTimeout()); sock.setReuseAddress(socketConfig.isSoReuseAddress()); sock.setTcpNoDelay(socketConfig.isTcpNoDelay()); sock.setKeepAlive(socketConfig.isSoKeepAlive()); if (socketConfig.getRcvBufSize() > 0) {
sock.setReceiveBufferSize(socketConfig.getRcvBufSize());
}
if (socketConfig.getSndBufSize() > 0) {
sock.setSendBufferSize(socketConfig.getSndBufSize());
}
final int linger = socketConfig.getSoLinger();
if (linger >= 0) {
sock.setSoLinger(true, linger);
}
conn.bind(sock);
final InetSocketAddress remoteAddress = new InetSocketAddress(address, port);
if (this.log.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.log.debug("Connecting to " + remoteAddress);
}
try {
sock = sf.connectSocket(
connectTimeout, sock, host, remoteAddress, localAddress, context);
conn.bind(sock);
if (this.log.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.log.debug("Connection established " + conn);
}
return; //连上主机后,就退出了
} catch (final SocketTimeoutException ex) {
if (last) {
throw new ConnectTimeoutException(ex, host, addresses);
}
} catch (final ConnectException ex) {
if (last) { //连不上,假设也是最后一个可以尝试主机了,就退出了。
final String msg = ex.getMessage();
if ("Connection timed out".equals(msg)) {
throw new ConnectTimeoutException(ex, host, addresses);
} else {
throw new HttpHostConnectException(ex, host, addresses);
}
}
} catch (final NoRouteToHostException ex) {
if (last) {
throw ex;
}
}
if (this.log.isDebugEnabled()) { //尝试下一个主机
this.log.debug("Connect to " + remoteAddress + " timed out. " +
"Connection will be retried using another IP address");
}
}
4 no alternative certificate subject name matches
中文:使用了无效的安全证书。 该证书仅对下列域名有效
curl: (51) SSL: no alternative certificate subject name matches target host name
访问的域名应该匹配subject name中的任何一个。
总结:
1 尽可能熟悉自己所用的开源组件,并了解其版本变更, 有可能的话升级下老版本。
2 升级第三方库要仔细测试,单纯看文档,参考最佳实践完成的代码不见得实际生效,实际情况往往远比理论情况来的复杂。
3 不应该假设所有组件都严格遵循协议,应该以实际实现为准。